By Jerry Sutherin, CEO at Young & Associates
Despite having limited requirements as defined by interagency guidance, the case can be made for requiring community financial institutions to have regular stress tests performed on their commercial real estate loan portfolios.
Emerging challenges in commercial real estate lending
Recent post-COVID events have resulted in a heightened concern with regulators as it relates to commercial real estate. Most notably, interest rates have increased 525 bps from March 2022 through July 2023. This correlates with the level of commercial loan delinquencies over that same period as noted in the chart below. This is further exacerbated the “work from home culture” and office vacancies increasing over the same period.
The ultimate impact on the commercial real estate sector is weaker NOIs, coverage ratios that are insufficient to meet loan covenants, higher Cap Rates and lower valuations. For those loans locked into a lower rate, the issue now becomes; what happens when loans mature or reset? That is occurring now.

Regulatory expectations for bank stress testing
Regulatory expectations for community bank stress testing initiatives have been set in both formal regulatory guidance and through more informal publications and statements. An interagency statement was released in May 2012 to provide clarification of supervisory expectations for stress testing by community banks.[1]
The issuance specifically stated that community banks are not required or expected to conduct the types of enterprise stress tests specifically articulated for larger institutions in rules implementing Dodd-Frank stress testing requirements, the agencies’ capital plan for larger institutions, or as described in interagency stress testing guidance for organizations with more than $10 billion in total consolidated assets.
OCC guidance on stress testing practices
However, in October 2012, the OCC provided additional guidance to banks on using stress testing to identify and quantify risk in the loan portfolio and to help establish effective strategic and capital planning processes.[2] The guidance reiterated that complex, enterprise-wide stress testing is not required of community banks. It also states that some stress testing of loan portfolios by community banks is considered to be an important part of sound risk management.
In the guidance, the OCC does not endorse a particular stress testing method for community banks; however, the guidance also discusses common elements that a community bank should consider, including asking plausible “what if” questions about key vulnerabilities; making a reasonable determination of how much impact the stress event or factor might have on earnings and capital; and incorporating the resulting analysis into the bank’s overall risk management process, asset/liability strategies, and strategic and capital planning processes.
The OCC bulletin also provides a simple example of a stress testing framework for community banks. In the summer of 2012, the FDIC also provided further guidance related to community bank stress testing in the Supervisory Insights Summer Edition.[3]
Interagency guidance on commercial real estate risk
Perhaps the most significant piece of guidance related to loan portfolio stress testing for community banks is the 2006 interagency Concentrations in Commercial Real Estate Lending, Sound Risk Management Practices.[4] The continuing importance of and regulatory emphasis on this guidance was made clear in December 2015 when the interagency Statement on Prudent Risk Management for Commercial Real Estate Lending[5] was released, which reiterated the importance of the principles described in the 2006 CRE Guidance.
The 2006 CRE Guidance describes several important practices for effectively managing the risks associated with CRE lending, especially concentration risk. Portfolio stress testing of the CRE portfolio is described as a critical risk management tool for institutions with CRE concentrations.
Examiner expectations for portfolio-level stress testing
While community banks have not been pushed to perform the enterprise-wide stress testing that the above guidance specifically states is not expected of them, examiner expectations for portfolio-level loan stress tests have continued to increase over time and are becoming more prevalent during a bank’s recurring exams. These expectations are centered on portfolios that represent significant concentrations and, given the perceived level of risk and the existence of the 2006 CRE Guidance, are therefore most focused on CRE portfolios.
A reasonable and well-documented approach to CRE portfolio stress testing, undertaken at appropriately frequent intervals such as on an annual basis, is the most effective way for community banks to meet examiner expectations and to contribute toward effective risk management of CRE concentrations.
Regulatory criteria for CRE concentration risk
The guidance also states that strong risk management practices (with stress testing being one of the most important) and appropriate levels of capital are important elements of a sound CRE lending program. Particularly when an institution has a concentration in CRE loans. It then lays out the criteria regulatory agencies utilize as a preliminary means of identifying institutions that are potentially exposed to significant CRE concentration risk:
- Total reported loans for construction, land development, and other land represent 100% percent or more of total capital, or
- Total commercial real estate loans (as described above) represent 300% or more of the institution’s total capital. The outstanding balance has increased by 50% or more during the prior 36 months.

The guidance is clear that these thresholds do not constitute limits on an institution’s lending activity and are instead intended to function as a high-level indicator of institutions potentially exposed to CRE concentration risk. Conversely, being below these thresholds also does not constitute a “safe harbor” for institutions if other risk indicators are present such as poor underwriting or poor performance metrics such as deteriorating risk rating migration and delinquency.
Case study: Loan portfolio concentration levels
As noted in the example above, the figures indicate that the bank does not have a high level of construction, and land development loans as the balances do not exceed the 100% threshold level as a percentage of total capital. However, the Bank has exceeded the 300% threshold of non-owner-occupied real estate loans as calculated under the 2006 CRE Guidance. Additionally, the Bank’s three-year growth rate in this category was 72.7%, which is greater than the 50% reference level that constitutes the second part of the two-part regulatory test for a heightened concentration in this category.
Impact of loan acquisitions
It should also be noted that regulatory guidance does not differentiate between organic growth and commercial real estate growth via acquisition. Therefore, all such loans acquired does impact the ratios noted in the concentration chart above.
Loss estimation in bank stress testing
The basic premise for any stress test modeling is to identify moderate / high loss estimates. Then look at the impact to capital on a loan-level basis as well as portfolio-wide. While some community banks provide some stress testing on a transactional basis at origination, the output is typically limited to scenarios that focus primarily on future interest rate fluctuations.
CRE stress test modeling, on the other hand, allows for an organization to gauge potential losses of the CRE portfolio using internal core loan-level data as well as call report data while factoring in other variables that could influence the ultimate collectability of commercial real estate loans.
Loan-level or bottom-up stress testing
The bottom-up or loan-level portion of the stress test estimates losses under the stress scenarios on a loan-by-loan basis. The loan selection is typically a function of the desired penetration identified by the organization. It’s comprised mostly of larger transactions with a sampling of newer originations and adversely risk rated transactions.
In this portion of the analysis, various stress factors are applied to the NOI, collateral value, and interest rate for each loan identified by the Bank. This information, coupled with the transaction’s debt service coverage, liquidation costs and Cap Rates help form a possible loan-level loss for each loan in moderate and in moderate and high-risk scenarios.
Top-down stress testing
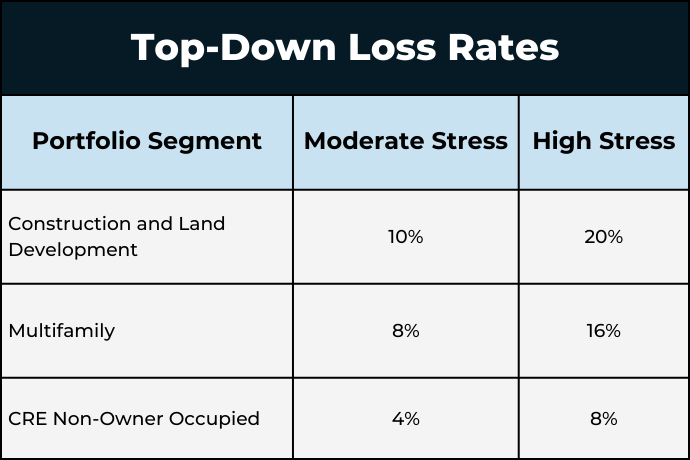
To ensure that the entire CRE portfolio is stressed, a useful model would use a top-down loss estimation method to “fill in” losses on the remaining portfolio for which loan-level information was not provided. This is accomplished by comparing the total balances for which loan-level data was provided in each of the various categories (construction and land development, multifamily, and all other non-owner occupied CRE) to the Bank’s call report. Losses are estimated on the amount of exposure for which loan-level information was not provided by applying a top-down loss rate.
The Moderate and High Stress Scenarios below are determined by applying the loss rates included in the stress test example in the 2012 OCC guidance on community bank stress testing. These loss rates represent two-year loss rates, consistent with the OCC’s stress testing guidance.
Enhancing portfolio oversight and credit risk management
Collectively, the “bottom-up (loan level)” and “top-down” moderate and high stress scenarios provide a global overview of a bank’s CRE portfolio and its potential impact to capital. Knowing that this is not a replacement for an enterprise-wide stress test. However, it allows a bank to provide its management, board of directors and regulators with some context of the estimated losses in this segment of their loan portfolio. It also serves as an effective supplement to their internal or third-party loan review.
Historically speaking, any situation in which significant weakness is experienced in critical market and economic factors will result in credit losses that are elevated above those that a bank experiences in “normal” times if unprepared. There is no replacement for appropriate credit administration, however all banks should always utilize tools such as stress testing to enhance their oversight of the metrics behind their CRE portfolio.
Financial institution performance and ultimately their ongoing safety and soundness are dependent on the performance of the Bank’s CRE portfolio. It is critical that management and the board of directors ensure that the bank emphasizes effective implementation of the risk management elements discussed in the 2006 CRE Guidance. These elements include:
- Continued effective board and management oversight,
- Effective portfolio management,
- Ensuring that management information systems are able to provide the information necessary for effective risk management,
- Performing periodic market analysis and stress testing,
- Regularly evaluating the appropriateness of credit underwriting standards, and
- Maintaining an effective credit risk review function
If a financial institution is successful in these endeavors, their CRE loan portfolio should continue to contribute positively to their performance. Accordingly, I am a proponent of all community financial institutions having a stress test performed regularly. This helps to ensure the performance of that segment of their loan portfolio as well as the entire organization.
Partner with Young & Associates for expert CRE stress testing
Navigating the complexities of commercial real estate stress testing can be challenging, especially with evolving regulatory expectations and economic uncertainties. At Young & Associates, we offer specialized CRE and Ag portfolio stress testing services designed to address these very challenges. With over 45 years of experience, our team understands the intricacies of regulatory guidance. We can provide your community bank with the insights needed to enhance strategic and capital planning.
Our proven stress testing model assesses the potential impacts of adverse economic conditions. This helps you manage risk effectively and comply with regulatory expectations. We provide actionable insights to guide your loan product design and underwriting standards. This eases the burden of stress testing and supporting your institution’s resilience.
Choose Young & Associates for a partnership that combines deep industry knowledge with a commitment to excellence. Let us help you stay ahead of regulatory demands and strengthen your CRE portfolio management. Reach out to us now to schedule a consultation.
[1] FDIC, PR 54-2012, “Statement to Clarify Supervisory Expectations for Stress Testing by Community Banks.” May 14, 2012.
[2] OCC Bulletin 2012-33, “Community Bank Stress Testing: Supervisory Guidance.” October 18, 2012.
[3] FDIC “Supervisory Insights, 9(1).” Summer 2012.
[4] FDIC FIL-104-2006, OCC Bulletin 2006-46, FRB SR 07-1, “Concentrations in Commercial Real Estate Lending, Sound Risk Management Practices.“ December 12, 2006.
[5] FDIC FIL-62-2015, OCC Bulletin 2015-51, FRB SR 15-17, “Statement on Prudent Risk Management for Commercial Real Estate Lending.“ December 18, 2015.