By Craig Horsch, Consultant, Young & Associates
Overview of Federal Crop and Livestock Insurance programs
Federal Crop Insurance and Federal Livestock Insurance are supplemental insurances that cover losses which are unavoidable and caused by naturally occurring events. They do not cover losses resulting from negligence or failure to follow good farming practices related to crops and/or livestock.
Federal Crop Insurance Programs include three main programs—Price Loss Coverage (PLC), Agriculture Risk Coverage (ARC), and the Marketing Assistance Loan Program (MALP)—as well as the Whole-Farm Revenue Protection Plan 2025 (WFRP), per the USDA Risk Management Agency.
-
PLC overview:
PLC program payments are issued when the effective price of a covered commodity is less than the effective reference price for that commodity. The effective price is defined as the higher of the market year average price (MYA) or the national average loan rate for the covered commodity. PLC payments are made to owners of historical base acres and are not tied to the current production of covered commodities. Covered commodities include wheat, corn, sorghum, barley, oats, seed cotton, long- and medium-grain rice, certain pulses, soybeans/other oilseeds, and peanuts.
-
ARC overview:
There are two types of Agriculture Risk Coverage: Agriculture Risk Coverage–County (ARC-CO) and Agriculture Risk Coverage–Individual (ARC-IC).
- The ARC-CO program provides income support tied to the same historical base acres—not current production—of covered commodities. ARC-CO payments are issued when the actual county crop revenue of a covered commodity is less than the county ARC-CO guarantee for that commodity.
- ARC-IC provides income support based on a farm’s revenue from current production of covered commodities, compared with a benchmark average of that farm’s production of those commodities. However, payments are limited to a portion of the farm’s historical base acres. This page focuses on ARC-CO; the ARC-IC program has not been widely adopted.
-
MALP overview:
The MALP allows producers to use eligible commodities they have produced as collateral for government-issued loans. Eligible commodities include wheat, corn, sorghum, barley, oats, upland and extra-long-staple cotton, long- and medium-grain rice, soybeans and other oilseeds, certain pulses, peanuts, sugar, honey, wool, and mohair.
-
WFRP overview:
WFRP insurance provides coverage against the loss of revenue that you expect to earn or obtain from commodities you produce or purchase for resale during the insurance period, all under a single insurance policy. WFRP offers benefits such as:
- A range of coverage levels from 50% to 85% to fit the needs of more farming and ranching operations;
- Replant coverage for annual crops, except Industrial Hemp;
- The ability to consider market readiness costs as part of the insured revenue;
- Provisions to adjust the insurance guarantee to better fit expanding operations;
- An improved timeline for farming operations that operate as fiscal year filers; and
- Streamlined underwriting procedures based on the forms used for WFRP.WFRP is designed to meet the needs of highly diverse farms that grow a wide range of commodities and sell to wholesale markets. The WFRP policy was specifically developed for farms that market directly to local or regional buyers, sell through identity-preserved channels, and produce specialty crops, animals, and animal products. The amount of farm revenue you can protect with WFRP insurance is the lower of the revenue expected on your current year’s farm plan or your five-year average historic income, adjusted for growth. This represents an insurable revenue amount that can reasonably be expected to be produced on your farm during the insurance period. All commodities produced by the farm are covered under WFRP, except timber, forest and forest products, and animals used for sport, show, or as pets.It is important to understand that WFRP covers revenue produced during the insurance period. For example, if a calf weighs 800 pounds at the beginning of the insurance period and is sold at 1,200 pounds during the insurance period, the value of production will be the additional 400 pounds gained. Inventory adjustments are used to remove production from previous years and to add revenue for production that has not yet been harvested or sold.
Understanding USDA Livestock Insurance programs
Per the USDA Risk Management Agency website, the Federal Livestock Insurance Programs are as follows:
-
Livestock gross margin – Cattle:
The LGM for Cattle Insurance Policy provides protection against the loss of gross margin (market value of livestock minus feeder cattle and feed costs) on cattle. The indemnity at the end of the 11-month insurance period is the difference, if positive, between the gross margin guarantee and the actual gross margin. The LGM for Cattle Insurance Policy uses futures prices to determine both the expected and actual gross margins. Adjustments to futures prices are based on state- and month-specific basis levels. The price the producer receives at the local market is not used in these calculations.
Eligible producers are those who own cattle in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming. Only cattle sold for commercial or private slaughter — primarily intended for human consumption—and fed in one of the eligible states are covered under the LGM for Cattle Insurance Policy.
-
Livestock gross margin – Dairy Cattle:
The LGM for Dairy Cattle Insurance Policy provides protection against the loss of gross margin (market value of milk minus feed costs) on milk produced from dairy cows. The indemnity at the end of the eleven-month insurance period is the difference, if positive, between the gross margin guarantee and the actual gross margin. The LGM for Dairy Cattle Insurance Policy uses futures prices for corn, soybean meal, and milk to determine the expected and actual gross margins. The price the producer receives at the local market is not used in these calculations.
Any producer who owns dairy cattle in the contiguous 48 states is eligible for LGM for Dairy Cattle Insurance Policy coverage. Only milk sold for commercial or private sale—primarily intended for final human consumption—from dairy cattle fed in any of the eligible states is covered under this policy.
-
Livestock gross margin – Swine:
The LGM for Swine Insurance Policy provides protection against the loss of gross margin (market value of livestock minus feed costs) on swine. The indemnity at the end of the 6-month insurance period is the difference, if positive, between the gross margin guarantee and the actual gross margin. The LGM for Swine Insurance Policy uses futures prices to determine both the expected and actual gross margins. The price the producer receives at the local market is not used in these calculations.
Any producer who owns swine in the 48 contiguous states is eligible for LGM for Swine insurance coverage. Only swine sold for commercial or private slaughter—primarily intended for human consumption—and fed in the 48 contiguous states are eligible for coverage under the LGM for Swine Insurance Policy.
Policy outlook: Projected spending impacts of proposed PLC and ARC-CO changes
In light of potential 2025 farm policy changes, the article “Spending Impacts of PLC and ARC-CO in the House Agriculture Reconciliation Bill” by Schnitkey, Paulson, Coppess (University of Illinois), and Zulauf (Ohio State University), published in farmdoc daily, offers valuable insight into the budgetary and structural implications of proposed revisions to two cornerstone commodity programs: Price Loss Coverage (PLC) and Agricultural Risk Coverage at the County Level (ARC-CO).
Key proposed changes
Under the House Agriculture Reconciliation Bill, four primary changes to PLC and ARC-CO are proposed:
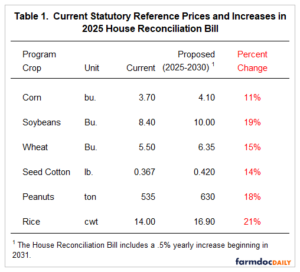
1. Statutory reference price increases:
From 2025 to 2030, statutory reference prices for major program crops would increase—for example, from $3.70 to $4.10 per bushel for corn (an 11% increase), from $8.40 to $10.00 for soybeans (19%), and from $5.50 to $6.35 for wheat (15%). Similar increases are also proposed for seed cotton, rice, and peanuts (Schnitkey et al., 2025, Table 1).
2. PLC payment floor adjustments:
The bill proposes new price floors for PLC payments—$3.30 for corn and $0.30 per pound for seed cotton—to limit downside price risk. These new thresholds would reduce outlays in low-price environments by capping PLC payment escalation.
3. ARC-CO enhancements:
Changes to ARC-CO include increasing the coverage level from 86% to 90% and the maximum payment rate from 10% to 12.5% of benchmark revenue, making the program more responsive during periods of reduced revenue.
4. Loan rate increases:
The bill also proposes a 10% increase in the loan rates for the six largest program crops, further enhancing the income safety net (Schnitkey et al., 2025).
Budgetary and distributional impacts
The authors estimate that these program changes would raise federal outlays for PLC, ARC-CO, and marketing loan programs from $46.5 billion to $76.4 billion between 2025 and 2035—a 64% increase (Schnitkey et al., 2025, Table 2). However, this increase is not evenly distributed across commodities or regions:
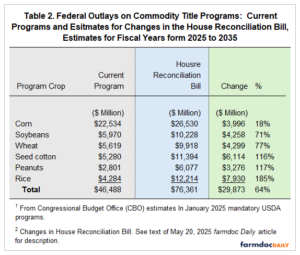
- Southern crops—notably peanuts, rice, and seed cotton—would see the largest increases in payments per base acre. In contrast, traditional Midwestern crops such as corn and soybeans would receive more modest increases.
- For farms with 500 base acres, estimated average annual payments under the proposed changes would be:
- Corn: $15,500
- Soybeans: $10,500
- Wheat: $8,500
- Seed cotton: $45,000
- Rice: $128,000
- Peanuts: $134,000 (Schnitkey et al., 2025, Table 2; Figure 1)
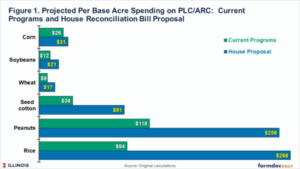
This disparity stems from differences in statutory reference prices across crops. Southern crops historically have higher relative reference prices, leading to larger government payments — an imbalance that would be widened under the proposed bill (Schnitkey et al., 2025).
Political and policy implications
To fund these increased outlays, the House Agriculture Committee is proposing spending reductions from the Nutrition Title, particularly the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP). This cost-shifting pits agricultural and nutrition interests against each other and introduces politically sensitive trade-offs that could impact the outcome of future Farm Bill negotiations (Schnitkey et al., 2025).
Why this matters
For agricultural lenders and risk managers, particularly those serving Midwestern crop producers, the proposed updates could affect the farm income landscape, collateral valuations, and overall credit risk. Although support increases are significant for crops like rice and peanuts, the more moderate gains for corn and soybeans mean Midwest producers may see less benefit from the bill in its current form. Understanding the potential outcomes of these policy shifts can help financial institutions refine their risk assessments and prepare clients for what lies ahead.
Staying ahead in a changing agricultural risk landscape
As federal crop and livestock insurance programs evolve — and legislative proposals like those in the 2025 House Agriculture Reconciliation Bill signal substantial shifts in farm subsidy distribution — lenders must be prepared to navigate increased complexity in agricultural credit risk. From changes in PLC and ARC to adjustments in federal loan programs and WFRP, these developments have direct implications for borrower cash flow, collateral valuation, and overall lending strategy.
For financial institutions serving agricultural clients, now is the time to reassess risk management frameworks, update lending practices, and evaluate credit exposures in light of these changes.
Young & Associates has deep expertise in agricultural lending and credit risk analysis. Our team can help your institution proactively adapt, with services that include portfolio review, credit risk management consulting, and tailored support for ag-specific lending challenges. Whether you’re seeking to strengthen underwriting processes or prepare for policy-driven shifts in borrower performance, we’re here to help you respond with confidence.
Explore our lending and credit risk consulting services to learn how we can support your institution’s success in this evolving environment.
References
Coppess, J., C. Zulauf, G. Schnitkey, N. Paulson and B. Sherrick. “Reviewing the House Agriculture Committee’s Reconciliation Bill.” farmdoc daily (15):89, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, May 14, 2025. Permalink
Kalaitzandonakes, M., B. Ellison, T. Malone and J. Coppess. “Consumers’ Expectations about GLP-1 Drugs Economic Impact on Food System Players.” farmdoc daily (15):49, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, March 14, 2025. Permalink
Schnitkey, G., N. Paulson, C. Zulauf and J. Coppess. “Price Loss Coverage: Evaluation of Proportional Increase in Statutory Reference Price and a Proposal.” farmdoc daily (13):203, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, November 7, 2023. Permalink
Schnitkey, G., C. Zulauf, K. Swanson, J. Coppess and N. Paulson. “The Price Loss Coverage (PLC) Option in the 2018 Farm Bill.” farmdoc daily (9):178, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, September 24, 2019. Permalink
Schnitkey, G., N. Paulson, C. Zulauf and J. Coppess. “Spending Impacts of PLC and ARC-CO in House Agriculture Reconciliation Bill.” farmdoc daily (15):93, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, May 20, 2025. Permalink